Introduction

The Internet has become an integral part of our lives. From social media to online shopping, we rely on the web for almost everything. But what if the Internet could be even more decentralized, open, and user-centric? That's where Web 3.0 comes in.
Also known as the semantic web, it is the next Internet generation. It's built on blockchain technology, allowing secure and transparent transactions. Unlike the current centralized web, where a few large corporations control most of the data, Web 3.0 puts power back into the hands of users.
If you're looking for a web application development company to stay ahead of the curve, it's essential to understand Web 3.0. It offers exciting opportunities for developers to create innovative and decentralized applications.
By hiring skilled Web 3.0 developers, your company can tap into the potential of this revolutionary technology and build cutting-edge solutions for your clients.
In this article, we will explore the evolution of the World Wide Web that led to the introduction of Web 3.0. We will also navigate this technology’s impact, challenges, and future.
Read along to understand the importance and potential of Web 3.0 in boosting the performance of modern-day businesses.
Understanding Web 3.0
While there's no single inventor of Web 3.0, the concept has evolved, drawing inspiration from various ideas and technologies. The term "Web 3.0" was first coined in 2001 by Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web.
There is no concrete definition of Web 3.0, except that it is based on a future internet where data would be more connected and machine-readable. Hence, it allows for a more intelligent and personalized web experience.
Building upon the foundations of Web 1.0 and Web 2.0, the technological concept of Web 3.0 aims to create a decentralized and open user experience. It leverages blockchain technology to ensure security, transparency, and decentralization.
What is Web 3.0?
It is the third generation of the World Wide Web, using 3.0 technology to create a more decentralized web browser experience. The integration of artificial intelligence makes it a smarter choice for handling 3.0 applications.
Let’s look deeper into the concept of Web 3.0 and its evolution from the predecessor versions of the World Wide Web.
The Evolution of the Web: From Web 1.0 to Web 3.0
The web has undergone significant transformations, from the early days of static websites to the interactive platforms of today. Let's journey through the Web's evolution from Web 1.0 to Web 3.0.
Web 1.0 (1990s)
- Read-only web: Primarily consisted of static websites with limited interactivity.
- Information dissemination: Focused on providing information to users.
- Example: Early websites like Yahoo! and Netscape.
Web 2.0 (2000s)
- User-generated content: Enabled users to create and share content.
- Social media: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube emerged.
- Web applications: Interactive web-based applications like Google Docs and Gmail.
Web 3.0 (Present and future)
- Decentralized web: Shifts power away from centralized authorities.
- Blockchain technology: Underpinning technology for secure and transparent transactions.
- Semantic web: Machines can understand and interpret information.
- AI integration: Artificial intelligence enhances user experiences and capabilities.
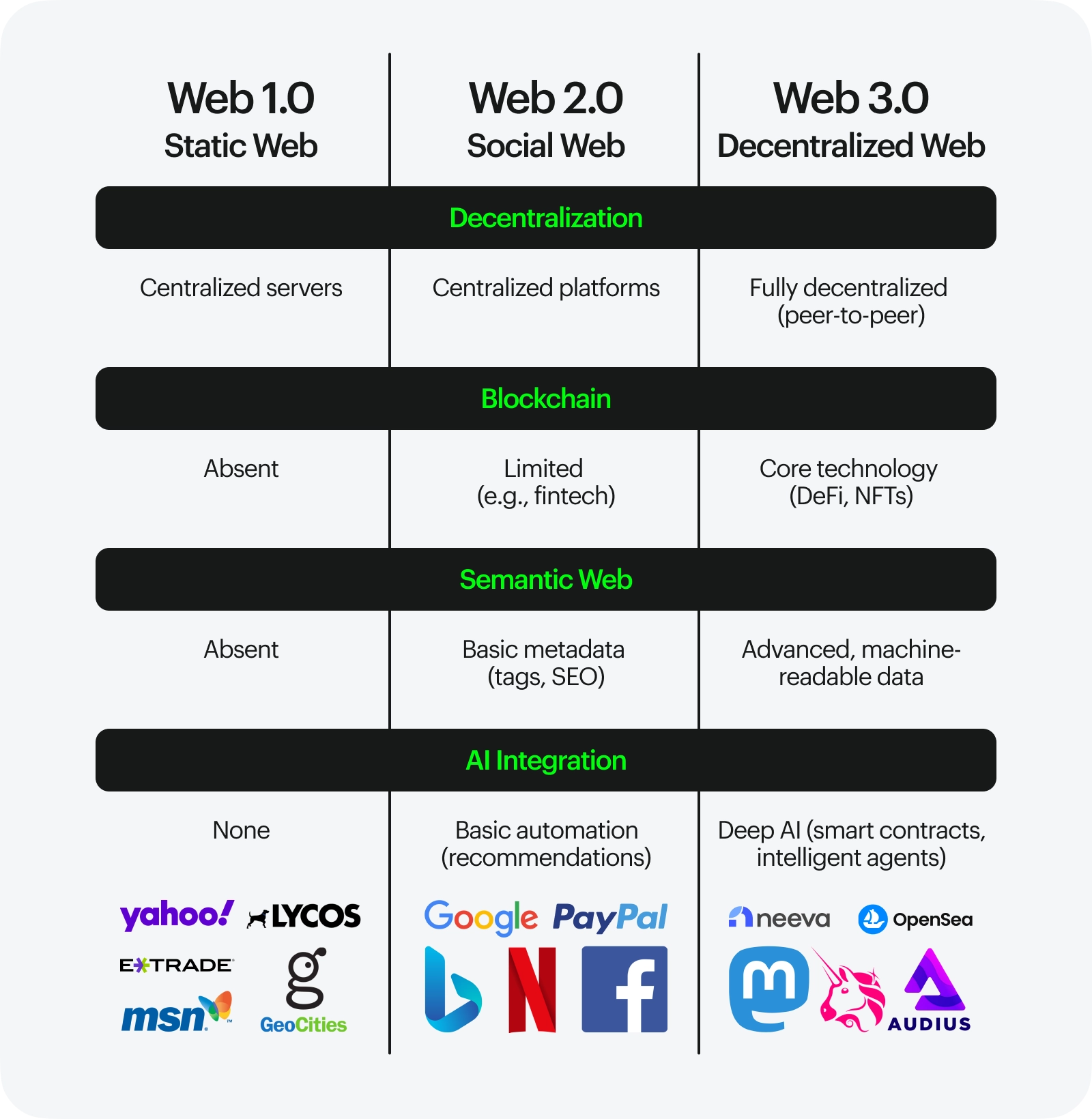
The differences are summarized in the table below:
| Feature | Web 1.0 | Web 2.0 | Web 3.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nature | Read-only | Read-write | Read-write-own |
| Control | Centralized | Centralized | Decentralized |
| User Interaction | Limited | High | Very high |
| Content | Primarily static | User-generated | User-generated and machine-readable |
| Technology | HTML | HTML, CSS, JavaScript | Blockchain, AI, IoT |
| Examples | Early websites, online encyclopedias | Social media, blogs, e-commerce | Decentralized finance, NFTs, metaverse |
| Key Focus | Information dissemination | User interaction and collaboration | Data ownership and decentralization |
Key Features of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 has several key features that set it apart from its predecessors. Some key features that must be highlighted include:
1. Decentralization
It distributes power among users, reducing the central authority of a few large corporations. Web 3.0's decentralized data makes it difficult to censor content, enhancing security with a reduced risk of data breaches and attacks.
2. Blockchain
Blockchain technology acts as a distributed ledger and provides a secure and transparent way to record transactions. It also enables the creation of ‘smart contracts’ to automate processes. Blockchain facilitates the tokenization of assets, representing ownership or value through digital tokens.
3. Semantic web
Web 3.0 offers a semantic web experience, presenting information in a machine-readable format for web content. It ensures an enhanced search with more accurate and relevant results, thus offering seamless integration between decentralized web apps.
4. AI integration
Artificial Intelligence AI provides an enhanced user experience with personalized content and recommendations. Machine learning and natural language processing enable machines to understand human language for more intuitive user interactions. AI integration also facilitates the automation of processes for improved efficiency.
Overall, Web 3.0 represents a significant leap forward in the evolution of the Internet. It takes control of web information from one governing body to give users greater autonomy over their data. User-generated content is expected to transform the web experience for businesses and their audiences.
The Role of Blockchain in Web 3.0
Blockchain technology makes the decentralized autonomous structure of Web 3.0 possible. It makes peer-to-peer transactions possible in real-time, removing the need for communication and information exchange intermediaries.
The generated content and data are stored across multiple nodes on a network, operating as a distributed ledger. Hence, no single entity owns the information. By leveraging blockchain technology, Web 3.0 aims to create a more secure, transparent, and user-centric internet.
Decentralization: A Core Principle of Web 3.0
Decentralization is a key concept in Web 3.0. It refers to the distribution of power and control away from centralized authorities. No single entity has complete control in a decentralized system, leading to a more democratic and resilient network.
Importance of Decentralization in Web 3.0
- Resistance to Censorship: Since data is spread across multiple nodes, manipulating or removing information becomes challenging, thus mitigating censorship.
- Increased Security: It reduces the risk of data breaches and attacks. If one node is compromised, the overall system remains secure.
- Enhanced Privacy: Giving users more control over their data protects their privacy and prevents it from being exploited. When data is stored and controlled by users rather than centralized entities, it is less vulnerable to misuse.
- Empowerment: It puts power back into the hands of users, allowing them to participate more actively in the network and make decisions about their data and how it is used.
Some common examples of decentralized applications utilizing these benefits of Web 3.0 include:
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are unique digital assets representing art, collectibles, or virtual real estate ownership. Examples include OpenSea and Rarible.
- Decentralized Social Networks - Decentralized social networks like Mastodon and Diaspora give users more control over their data and interactions.
- Decentralized Content Distribution - Decentralized content distribution platforms allow users to share and access content without relying on centralized servers. Common examples include IPFS and Filecoin.
While these are a few examples of decentralized applications, as technology evolves, we can expect to see even more innovative and disruptive dApps emerge.
Security and Privacy in Web 3.0
Web 3.0 offers significant improvements in security and privacy compared to previous web versions. While Web 1.0 provides a static secure environment and Web 2.0 introduced significant security and vulnerability issues, Web 3.0 technology has risen to address those concerns.
It leverages natural language processing and blockchain technology to provide a decentralized approach to handling power and data in a web system. Thus making it difficult for malicious actors to target a single point.
With greater user control over data and improved transparency, Web 3.0 offers enhanced security and privacy compared to its predecessors. This shift towards a more decentralized and privacy-focused internet is a significant step forward in ensuring the protection of user information.
How Web 3.0 Will Impact Various Industries?
While understanding the impact of Web 3.0 on creating a more personalized user interaction and secure search engines, let’s examine its effect on different industries.
1. Financial Services and Cryptocurrencies
Web 3.0 has revolutionized the financial services industry. Its significant impact is seen in cryptocurrencies and Decentralized Finance (DeFi).
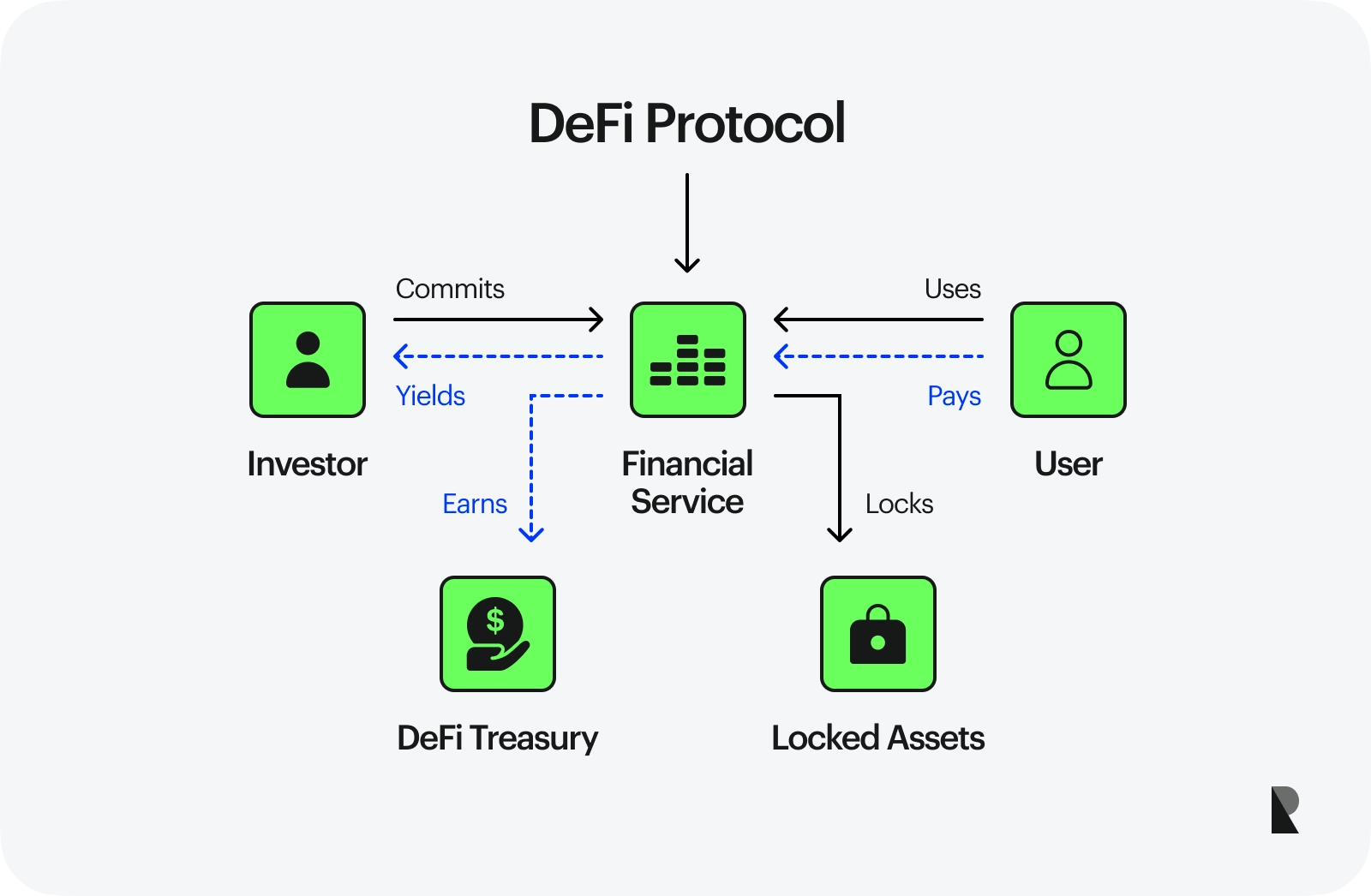
A review of the decentralized finance ecosystems (MDPI)
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies operate on blockchain networks, creating the concept of decentralized digital currencies. Hence, currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum can operate without the dependence of intermediaries like banks.
Cryptographic algorithms provide robust security to protect transactions from fraud and censorship. Hence, users' personal information and financial data are enhanced in terms of security.
Web 3.0 also creates global accessibility for cryptocurrencies, enabling users to access their finances from mobile devices anywhere. It breaks down geographical barriers, leading to financial inclusion on a wider scale.
It also ensures greater transparency for users to track their transactions and verify their authenticity.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
It refers to platforms allowing users to lend, borrow, or trade cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. Some common DeFi platforms include Aave, Compound, and Uniswap. The process becomes more user-friendly with Web 3.0 and its improved generated content on web pages.
Users gain more control over their financial assets. The ease of transactions allows for innovative financial products for asset management. With Web 3.0, these services also become easily accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
2. Healthcare
Alongside financial services, the technological advancement of Web 3.0 has also revolutionized healthcare, particularly in data storage and telemedicine.
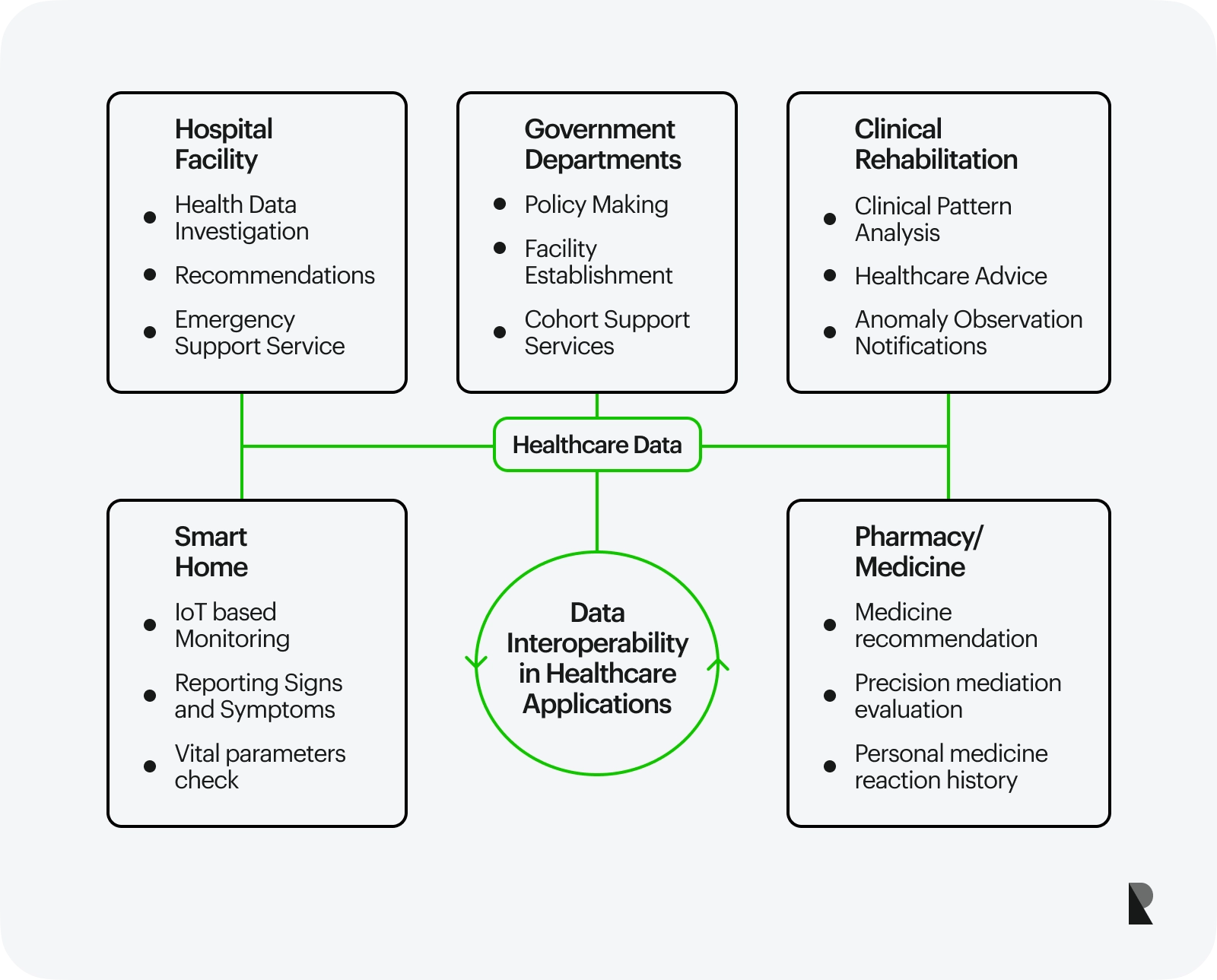
An outlook of healthcare systems in an intelligent environment (SpringerLink)
Secure Data Storage
The decentralization of information within the Web 3.0 architecture applies to patient data storage. It reduces the threat of data breaches and enhances patient privacy.
Once data is stored on a blockchain cannot be altered or deleted, providing a tamper-proof medical history record. The system's cryptographic algorithms protect patient data from unauthorized access and manipulation.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine is another area of healthcare that benefits from the integration of Web 3.0. Since telemedicine relies on digital media, social networks online, and AI, blockchain technology provides it with a significant boost.
It enables remote patient monitoring and virtual consultations. Patients can use wearable devices to track their vital signs and consult with their healthcare professionals. The architecture also allows secure data sharing and better coordination between patients and doctors.
These advancements lead to better patient outcomes, increased access to care, reduced costs, and enhanced patient privacy. By leveraging Web 3.0 technologies, healthcare provision is revolutionized, making it more accessible, efficient, and secure.
Web 3.0 will majorly impact industries like healthcare and finance by providing a more secure, robust, and accessible digital infrastructure for users.
Challenges of Web 3.0
The discussed examples show that Web 3.0 significantly impacts industries, social media, and users. However, it comes with its own set of challenges. Exploring the different hurdles to integrating these uses with Web 3.0 is equally important.
Technical and Adoption Challenges
Despite its promising potential, Web 3.0 faces several technical and adoption barriers that must be addressed. Let’s examine these challenges more closely.
Technical Barriers
Challenges within the technical side of Web 3.0 can be listed as follows:
- Scalability - Blockchain technology can need help handling large volumes of transactions, especially during peak times. This can lead to network congestion and increased transaction fees.
- Interoperability - Ensuring seamless communication and data exchange between blockchain networks and applications is a significant challenge. This lack of interoperability can hinder the growth of the Web 3.0 ecosystem.
- Complexity - The underlying technology of Web 3.0, including blockchain and smart contracts, can be complex for many users, making it difficult to understand and adopt.
- Security - While blockchain offers enhanced security, it is not immune to vulnerabilities. Attacks like phishing, hacking, and malware pose ongoing application threats.
Adoption Hurdles
The challenges continue beyond the technical side. There are issues associated with integrating Web 3.0 into a system as well. Some common adoption hurdles include:
- User Experience - Many Web 3.0 applications can be difficult for non-technical users, hindering adoption. User-friendly interfaces and simplified onboarding processes are essential.
- Regulation - The regulatory landscape is still evolving, creating uncertainty and potential barriers for businesses and developers. Clear and consistent regulations are needed to foster innovation and protect consumers.
- Education and Awareness - Raising awareness about Web 3.0 and its benefits is crucial for driving adoption. Educational initiatives can demystify the technology and encourage broader participation.
- Cost - The costs associated with developing and using Web 3.0 applications can be high, particularly for small businesses and individuals. Reducing these costs is essential for widespread adoption.
Need to understand these challenges and find ways to address them as a priority. Handling these barriers will be critical for the successful development and growth of Web 3.0.
The Future Vision of Web 3.0
As Web 3.0 evolves, we can anticipate several exciting trends and expectations. Driven by more user-friendly interfaces and integration with existing platforms, we can expect to see increased technology adoption.
With AI-powered tools enabling personalized recommendations and content, the generated content is also expected to enhance the overall user experience. The future also allows greater interoperability through standardized protocols and cross-chain bridges, creating a more interconnected ecosystem.
Beyond these trends, Web 3.0 is expected to unlock new use cases, such as supply chain transparency, decentralized identity, and immersive virtual worlds.
This increased use and integration of the technology will also lead to more transparent regulations and comprehensive regulatory frameworks. It will ensure improved and increased collaboration between regulators and the industry.
It is also important to address all associated ethical considerations. Everything needs to be carefully considered and addressed, from addressing privacy concerns to understanding the social and economic implications of Web 3.0.
Thus, Web 3.0 can potentially transform the Internet and revolutionize various industries. By addressing technical challenges, improving user experiences, and establishing a robust regulatory framework, we can unlock the full potential of this exciting technology.
Conclusion
Web 3.0 represents a paradigm shift in the Internet, offering a decentralized, open, and user-centric vision. Its underlying technology, blockchain, provides security, transparency, and immutability, giving new meaning to how we interact with online applications and services.
Common examples of applications of Web 3.0 include decentralized finance to non-fungible tokens and beyond. Hence, the technology has the potential to transform various industries. Web 3.0 aims to create a more equitable and innovative Internet by empowering users with greater control over their data and interactions.
As it continues to evolve, we expect to see a new definition of online experience develop with Web 3.0, shaping the future of the Internet and transforming how we live and work.
Sep 11, 2024
