WCAG Meaning in Web Accessibility, Design, and Development
Read about WCAG meaning and importance in web accessibility. Learn the principles of web accessibility and follow a checklist to improve the online presence.
Written by RamotionJul 18, 202221 min read
Last updated: Aug 29, 2024
Website design and development may seem a fairly simple task. However, there are several layers of complexity involved in the process. From selecting the right themes and designs to ensuring the functionality of every single element, it takes a lot of creativity and expertise in building a good website. In the modern marketplace, where every organization has to maintain a strong digital presence and the competition is always increasing, businesses cannot merely create content and assume that the website will perform well. There are several concerns for designers, developers, and content creators when working on a website design and development project. One such aspect is accessibility.
Irrespective of the different web technologies and the platforms used to design and host websites, accessibility barriers are a major concern. The users of the world wide web have varying physical and cognitive abilities because of which some of the content on the internet may not be equally accessible to everyone. However, any public-facing website should not discriminate against the users based on their disabilities or limitations. The use of design elements and the content presented on the websites should be such that it is accessible to everyone. This is why a modern user interface design company would always adhere to the principles of accessibility.
Are there any standards of accessible website design? If so, where do these standards come from, and why are they important? In this article, we address these questions by introducing Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). We describe the key principles for creating an accessible website, along with a checklist to keep in mind for future projects.
WCAG meaning
WCAG stands for Web Content Accessibility Guidelines. As the name indicates, it is a collection of guidelines designed to ensure equal access to digital content for the users. The first version of these guidelines was developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) in 1999. The standards are constantly updated as technology evolves and new needs arise with time. The latest version (2.1) of accessibility guidelines was launched in the year 2018 and an update to this version is scheduled for later this year.
What does WCAG mean?
WCAG stands for Web Content Accessibility Guidelines. It is a set of compliance principles designed for content creators and web developers to ensure that the digital content is accessible to the audience irrespective of their physical and cognitive limitations.
The standards set by WCAG ensure that web development does not discriminate against people with disabilities. No matter which assistive technologies are used by the audience, adhering to these standards can greatly improve the overall quality and performance of the content, from the perspective of accessibility. As we’ll discuss later, it is not only an ethical but a legal responsibility of all website designers and developers to make their digital content accessible to the target audience. Meeting the accessibility standards also improves the usability of a website, thus leaving a strong impact on the overall user experience.
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines do not merely enlist the rules and principles but W3C also provides an excessive checklist that the developers can use to make their content more accessible. Additionally, according to WCAG, there are three different levels of accessibility that the websites can aim to achieve.
WCAG compliance levels
There are three levels of WCAG compliance, based on the extent to which the web content is made accessible. WCAG levels are labeled as A, AA, and AAA in the increasing order of compliance. Level A has the minimum requirements and level AAA has the most number of criteria to be met.
Level A conformance
Level A is the minimum level of compliance required for any website to be accessible. There are 25 criteria that must be met for a website to conform to level A of WCAG. This level includes the basic features and alternative options that can ensure that a website can be accessed in a fairly good manner by individuals having physical or cognitive limitations.
For example, when it comes to video and audio content on a website, providing a transcript and synchronized captions or subtitles for any recorded content is one criterion for a website to conform to level A. It must be noted that this is only a single criterion. For a website to be granted the status of level A compliant, it must meet all the requirements listed in the WCAG for different types and modes of content.
Level AA conformance
The second or middle conformance level is labeled as AA. For a website to meet this level, 37 criteria must be met. The criteria for this level ensure better accessibility, thus creating an improved version of the web content.
Let’s take the same example of video and audio content on a website. For a website to conform to level AA success criteria, it must also provide synchronized captions or subtitles for all the live content. This means that if you’re hosting a live webinar and captions are generated in real-time, you are meeting one requirement of the AA level.
Level AAA conformance
WCAG Level AAA is the highest level of website accessibility. In most cases, it is the ideal that all websites may aim to achieve. The 60 criteria set for Level AAA conformance are not easy to meet. If, however, these criteria are met on any website, it will not be wrong to say that the website will be a remarkable example of accessible design.
Going back to the example of one criterion: audio and video content. Level AAA success criteria require that a sign language video is also provided along with any content that contains audio. This, along with the requirements of levels A and AA, will ensure that everyone gets equal access to digital content.
WCAG importance
Accessibility is one of the most important concerns for modern websites. Unfortunately, this is one of those aspects that often gets overlooked. While designers and developers are focusing on usability, aesthetics, and unique design elements on web pages, the attention given to accessible design is not as much as it should be. This is why a set of rules, standards, and principles is required so that the digital content is made available and accessible to all audience groups. Web Content Accessibility Guidelines cover all the necessary and essential elements for a website to ensure equal accessibility.
Is WCAG required?
WCAG is required for all online content, not just as an ethical responsibility but as a legal one as well. Accessibility guidelines are designed to ensure that no one is left behind in the digital environment.
There are several reasons why such guidelines are important for UI/UX designers and web developers. If, on the one hand, WCAG criteria ensure that the needs of the users are met in the best possible ways, then, on the other, these guidelines also increase the credibility of and loyalty to an organization. This is beneficial to the users as well as the businesses in today’s competitive environment. For a specific product or service, there are several alternatives available to the audience. If their needs are not met by one product, they can easily switch to another, where the design is more accessible, user-friendly, and helpful. A website that cares for the varying needs of its viewers is the one that performs well, and for good reason.
Follow the law
It might come as a surprise but the accessibility of websites is required by law. According to Title III of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), discrimination on the basis of disabilities is prohibited in all public spaces. Although this title does not explicitly refer to websites and online spaces, it is implied that all public websites are spaces where discrimination based on physical or cognitive limitations is prohibited.
When designers and developers follow the accessibility guidelines, they are, in fact, following the law and making accommodations for people who need some assistance. This is one of the most important reasons that digital content should always be made equally accessible to all audience groups.
Fulfill an ethical responsibility
On the one hand, there is the law, and on the other, there is the ethical and moral responsibility to help those who need special assistance. This, of course, is not just limited to UI/UX designers and is a common moral principle to be followed by everyone. The importance of this principle gets more pronounced in digital spaces where the differences are so subtle that they often go unnoticed.
By adhering to WCAG criteria, designers can ensure that the differences in the online world are reduced to some extent, if not entirely eliminated. The internet is a rich resource of knowledge and limiting access would put people with physical disabilities at a great disadvantage. For websites and digital content, accessibility involves the assurance that equality will be the top priority. This is what WCAG principles aim to achieve.
Reach a wider audience
One of the goals of every business is to increase the customer base and reach a wider audience. With the internet being available for individuals in all corners of the world, it becomes important for organizations to think about the varying needs of their target audience. If, for instance, a website’s content is not accessible with the help of a screen reader, this excludes a group of target customers with specific disabilities. The same goes for other limitations and challenges.
When websites adhere to the standards set in the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines, they overcome the challenge of excluding certain groups by being accessible to a wide range of audiences. This not only adds to the credibility of the organization but also brings more business, thus giving a competitive edge in the market.
Improve the user experience
The user experience of a website is about giving a lot of control to the audience so they can make the choices they want and accomplish their tasks. It is, in other words, about making the lives of the users easier without taking away control from their hands. This is where accessibility plays a vital role. Accessible designs provide users with multiple ways to access a given content and also ensure that there are alternatives available for them to mold the experience in ways that they are comfortable with.
For example, by creating the website in a way that the users can read the content themselves or have a screen reader do the job, they get control and variety. Similarly, by providing keyboard shortcuts, individuals with physical disabilities do not have to worry about using a mouse or trackpad. Such alternatives impact the overall experience, adding to the satisfaction of the target audience.
Adhere to the principle of simplicity
When a website is designed in a complicated way, the users get overwhelmed and are unable to accomplish their goals. This leaves a bad impact on the overall user experience, resulting in the loss of customers. It is, therefore, recommended that websites and mobile applications be designed with the important UX principle of simplicity in mind. Simple designs are often created using familiar design elements, so the users do not end up spending a lot of time learning a new experience.
When we look at WCAG principles, it is not hard to see that all the guidelines advocate simplicity. The use of simple fonts and easily distinguishable colors are important for the accessibility of web pages. This is also what simplicity in design is all about. Therefore, by following the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines, UI/UX designers can check the box of simple design from their list of design principles as well.
WCAG principles
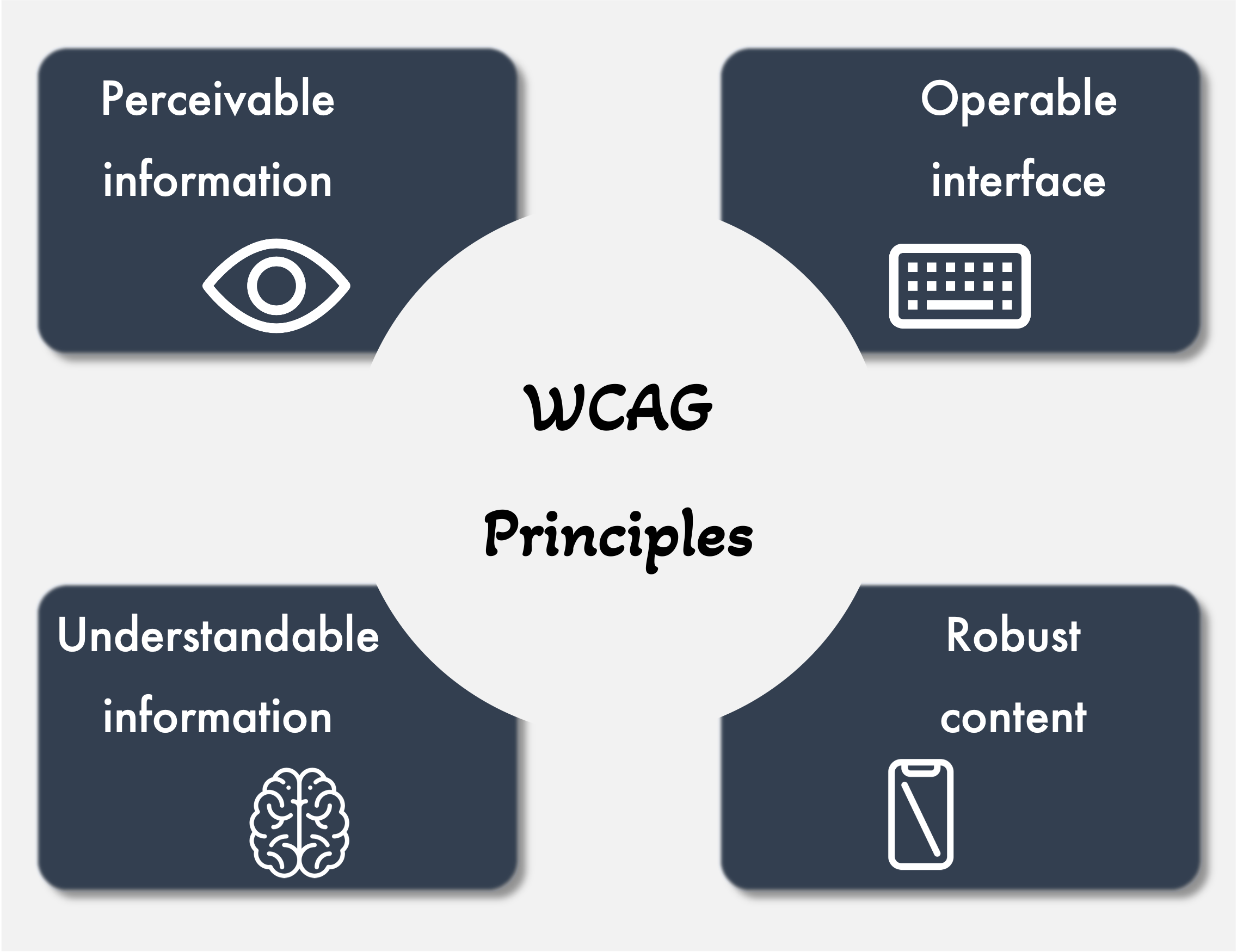
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines are based on four basic principles. It is essential for web developers to consider all of these aspects when designing content for any website. The principles that WCAG refers to encompass all the accessibility challenges that could typically be faced by the visitors of any website. When thinking about improving the accessibility compliance of any digital content, these four principles are the ones which all designers and developers should start from.
What are the WCAG guiding principles?
There are four WCAG principles to be kept in mind.
- Perceivable information
- Operable interface
- Understandable information
- Robust content
A great way to look at the WCAG guiding principles is from the perspective of empathy and user-centered design. When UI/UX designers and web developers put in the effort to be empathetic and considerate towards the target audience, that is when they start addressing their needs effectively. This is where WCAG plays a critical role. These principles provide a unique lens to designers using which they can improve their understanding of the target audience, feel their pain, and attempt to improve the overall user experience.
What follows is a small description of each principle and its role in making digital content more accessible.
1. Perceivable information
The first principle of WCAG is to create and ensure perceivable information. This means that the users should be able to use their senses without any obstacles when interacting with the content and design elements present on a website. If a group of website visitors is facing visual challenges, the platform should aid them in accomplishing their tasks by providing alternative options.
One example of making the digital content perceivable is providing text alternatives — or alt texts — with images, videos, and other media elements. Similarly, providing captions, subtitles, and transcripts improve the accessibility of the content, making it more perceivable.
2. Operable interface
The second principle of creating accessible content for websites is to make the interfaces operable. Websites built on the principle of creating an operable user interface make sure that the audience groups using assistive technologies get a seamless and satisfying experience, similar to every other user. This includes the use of screen readers, voice recognition, keyboard shortcuts, and other such alternatives.
One example of creating operable interfaces is the assurance that the web pages are compatible with screen readers. This ensures that when visually challenged users navigate the website, they can do so without any hassle.
3. Understandable information
One of the biggest challenges in modern web technologies is to create content that the users can understand in a clear manner. The importance of this factor gets more pronounced when we look at it from the perspective of accessibility because then we are not just looking at the use of plain and simple language. In this case, the designers and developers must ensure that the appearance of the content is also understandable. From familiar and simple navigation to better readability and simple fonts, all factors play a crucial role in making online information understandable and thus accessible.
One such example is the ways in which users can be guided to avoid errors and correct mistakes. For example, when a user clicks on or navigates to a page wrongly, they must have a way to go back or exit from the page without losing any progress on their task. This can be achieved by providing warnings, clear error messages, and proper instructions wherever possible.
4. Robust content
The last, and equally important, the principle of WCAG is ensuring the robustness of digital content. In today’s world, individuals use varying devices and technologies to browse the internet. The online content must ensure accessibility to a wide range of audiences, irrespective of the technologies and platforms they use. The screen size, operating system, and/or browser must not impact the presentation, understandability, and usefulness of the online content.
One common example of creating robust content for the internet is to ensure that the websites are responsive on mobile devices, such as tablets and smartphones, along with desktop and laptop devices. Additionally, a website must also be accessible using different operating systems and web browsers.
WCAG checklist
Along with the web accessibility principles, W3C also has a comprehensive checklist that designers and developers can follow to make the online content easily accessible. The WCAG guidelines checklist covers all the criteria enlisted in the A, AA, and AAA levels of conformity. UI/UX designers can follow these guidelines in all of their digital projects, particularly when it comes to the design and development of useful websites.
What are some of the guidelines for WCAG?
The following checklist can be extremely helpful for WCAG.
- Provide alternative text
- Include captions and transcriptions
- Use accessible fonts
- Provide options to resize text
- Give users control over the contrast
- Adjust the timing of the content
- Make the content accessible by keyboard
- Avoid flashing animations
- Provide descriptive titles
- Ensure appropriate headings
- Use descriptive anchor text
- Use plain language
- Provide options to change the language
- Ensure consistency in navigation
- Use familiar design patterns
However, the checklist provided by WCAG is a little too comprehensive. This means that for someone who is new to the concept of accessibility and accessible design, it can get a little overwhelming. The following checklist is adapted from the extended version provided by WCAG. This simplified version will get you started with accessibility guidelines and help you create quality content for your website projects.
1. Provide alternative text
One of the most important things to achieve in any web page is to provide alternative options to interact with the content. If an individual is using any assistive technology, such as screen readers, the website should have alternative text with media elements, so that they can navigate without any frustrations or lack of information.
2. Include captions and transcriptions
Audio and video elements on any webpage must be accompanied by captions, subtitles, and transcriptions. This provides a better experience for the audience who cannot hear the content. In the case of live videos, it may not be possible to provide synchronized captions. However, efforts should be made to provide some textual descriptions of the media content.
3. Use accessible fonts
An important concern in website design is the use of visual and textual elements in a way that the information is readable and understandable. The presentation of content is extremely crucial in this regard. This is where the importance of accessible fonts comes into play. When designing any website, fonts should be used such that the readability of the content is improved and individuals with any impairments do not struggle while navigating the website.
4. Provide options to resize text
Another important aspect of textual content is the font size. The content on the website should be presented such that the users have the option to resize the text. It must be noted that almost all browsers come with this option. Therefore, the task of designers is to ensure robustness here. This means that if the text is resized, it should not disrupt the interface of the website itself.
5. Give users control over the contrast
Visual elements, such as contrast and brightness, have a great impact on the accessibility of web content. UI/UX designers should ensure that the users have maximum control over these features and that the factors such as contrast, brightness, and choice of colors should be considered when designing a website. Here again, it is important to maintain the robust nature of digital content.
6. Adjust the timing of the content
Not all users need the same time to read or view every single element on a webpage. Individuals with learning disabilities, for example, may need longer to read the hover text. It is, therefore, important to adjust the timing of the dynamic content in a way that does not put anyone at a disadvantage. For WCAG compliance, make sure that your dynamic content appears for a significant amount of time on the screen and is easily understandable.
7. Make the content accessible by keyboard
If an audience group has specific physical limitations, they may not be able to interact with the online content using all the input devices. For example, if your website requires voice commands, individuals with speech disabilities will not be able to use it effectively. This is why WCAG requires that your content is accessible using a simple device, i.e. a keyboard.
8. Avoid flashing animations
Flashing images, gifs, and animations can be disturbing for some users. It is important that such content is avoided when designing a website. If it is absolutely necessary to include flashing content, a warning of some sort should be provided so the users avoid it if they are not comfortable.
9. Provide descriptive titles
One of the things that make websites findable on the internet and also accessible to the target audience is the use of descriptive titles. This information is valuable for the users as well as the organization owning the website as it improves search engine optimization (SEO). Make sure that the titles of all web pages are descriptive and provide some meaningful information to the audience.
10. Ensure appropriate headings
Along with titles and subtitles of pages, it is also essential to include appropriate headings on the web pages. Designers and developers should use HTML tags in a way that makes it easy for screen readers to go through the website, thus making it accessible. If appropriate heading tags are not used, the text will not be read as it is supposed to and will end up confusing the audience.
11. Use descriptive anchor text
Providing useful internal and external links on the website is always helpful for the target audience. However, it must be ensured that the links are linked to descriptive anchor text. This way, the screen readers are able to provide the information to the users in an understandable manner. If the anchor text is not there or is not descriptive enough, it can be confusing and frustrating for the target audience.
12. Use plain language
One of the most important aspects of online content creation is the use of plain and simple language. This is one of the factors that make the information readable and understandable at the same time. UX writers and content strategists need to make sure that all the content is written and presented in a simple manner that the users can relate to.
13. Provide options to change the language
Most online businesses today are dealing with a global audience. When designing content for such users, it is important to take regional factors into consideration. Language is an important factor that can improve the accessibility of a website. It is critical to mention the default language upfront and provide users with options to switch to a language of their choice. Small businesses may not be able to achieve this as it requires additional resources such as the help of translators. However, the aim should be to meet the needs of all audience groups.
14. Ensure consistency in navigation
Consistent design is always helpful and useful for the target audience. The impact of consistency in navigation is even more pronounced when dealing with the question of accessibility. Using consistent patterns, such as menu icons and scroll effects, is important for users. Similarly, navigation should also be made consistent on different devices and platforms to ensure better access to the content.
15. Use familiar design patterns
Design patterns are one of the most important user interface components. For individuals with physical and cognitive challenges, it is difficult to learn new patterns with every single website. Therefore, web designers should ensure that familiar design patterns are used for websites — ones that the audience is comfortable with. This is what makes the task of UI/UX designers challenging and rewarding at the same time, where they have to find the balance between creativity and familiarity.
Conclusion
Web content accessibility is an important concern as well as a challenge for modern organizations. In today’s world, where the internet is becoming a rich resource for knowledge and anyone without access to online content can fall behind in the advancing world, it is important that digital content be made accessible to everyone irrespective of their physical or cognitive abilities. It must be noted that the accessibility of online platforms is a legal, moral, and ethical responsibility, one that all leading businesses must fulfill.
Creating accessible websites is also critical for businesses, as this adds to their credibility, increases the loyalty of customers, and also helps them maintain a strong online presence. If businesses want to succeed in the competitive market, they must pay attention to widening their customer base, and one such way is to make the content accessible to everyone.
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines provide excellent standards and checklists for web designers and developers to improve the accessibility of their websites. There are also several platforms that web developers can use to make sure that they are adhering to the criteria set by W3C in their extensive guidelines. One such tool is WAVE WebAIM which can be used for WCAG testing. This tool highlights the issues and areas of concern on a website and also provides tips to improve the content.
Whether you’re new to UI/UX design or have been working on incredible projects for some time, accessibility is something that you should give due attention to. The principles, guidelines, and checklist gathered in this article are based on the standards set forth by WCAG. UI/UX designers can use these guidelines for their future products and play their part in making digital spaces accessible to everyone.