Introduction
Digital services and software applications are a necessary part of today’s enterprises. Businesses must develop, maintain, and manage an entire online infrastructure to provide customers with online services.
While there are different methods of executing these services, businesses aim to opt for cost-effective solutions for optimized results. Among these options are the technological approaches a cloud platform offers and Software as a Service (SaaS).
In this article, we will explore the details and differences between a cloud-based service and a SaaS application. We will also compare their business applications to determine the factors that determine which one is the most suitable approach.
Read along to navigate SaaS and cloud computing as you choose the best approach to maintain your online business applications.
Before we discuss the differences and benefits of both technological approaches, it is important to understand their basics.
Defining Cloud Computing

Cloud computing is a cloud-based service that runs on the cloud via the Internet. It allows businesses to provide services and applications online that can be accessed through any device without storing data on physical hard drives.
Hence, these cloud services provide on demand resources for businesses to manage their data and applications. Some common terms associated with cloud computing include:
- Virtualization: the creation of flexible and virtual versions of the hardware
- Service-oriented architecture: breaks down applications into modular components for easy cloud deployment
- Distributed computing: leverages the power of multiple computers to execute tasks
What is Cloud Computing?
It is a cloud based service that provides on-demand computing resources to businesses based on three main service models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
Based on these key technologies and their uses, cloud computing services are divided into three categories for businesses to choose from. These classifications are as follows:
- IaaS - Infrastructure as a Service: Businesses rent virtual computing resources like servers and storage from their cloud provider.
- PaaS - Platform as a Services: Enterprises rent a complete cloud platform including an operating system, a programming language, and development tools.
- SaaS - Software as a Service: Organizations rent software applications from a third party provider.
Other aspects of cloud computing include private and public clouds and a mix of both called hybrid cloud environments. While public cloud services are more commonly accessible, cloud computing also includes cloud-native applications designed specifically for cloud-based infrastructure.
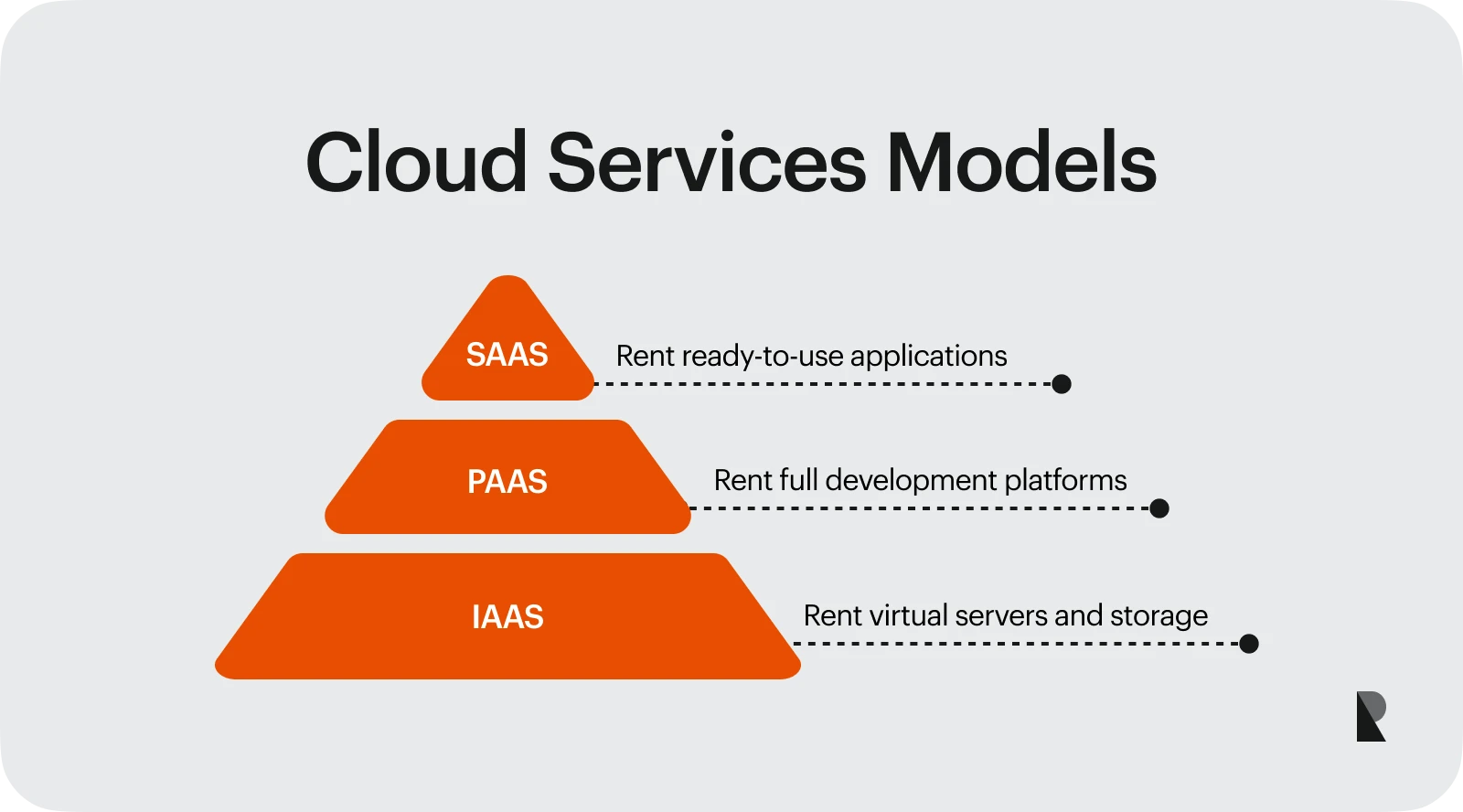
All variations of cloud computing aim to provide a flexible and scalable environment for businesses to develop and manage their resources online.
Defining Software as a Service (SaaS)

SaaS is a service model provided under the broader entity of cloud computing. It refers to a model allowing businesses to rent software applications run on a cloud environment. It eliminates the need to run applications on company computers and data centers.
Since SaaS applications are handled by a third-party provider, the cloud provider manages everything, from the server it runs on to the software to its security. The organization simply gets access to the required software application with a subscription fee.
Let's compare the SaaS model’s key aspects with the traditional software delivery model to gain a better understanding.
- Delivery and access: While SaaS is accessible via a browser or app on the Internet, traditional software requires product purchase and download directly to a computer system.
- Cost and investment: While the traditional approach requires a large license fee to purchase the software, a SaaS vendor charges a recurring fee under a subscription model.
- Maintenance and updates: Unlike a traditional approach where you must manage installation and updates, SaaS providers handle all maintenance, updates, and security patches where needed.
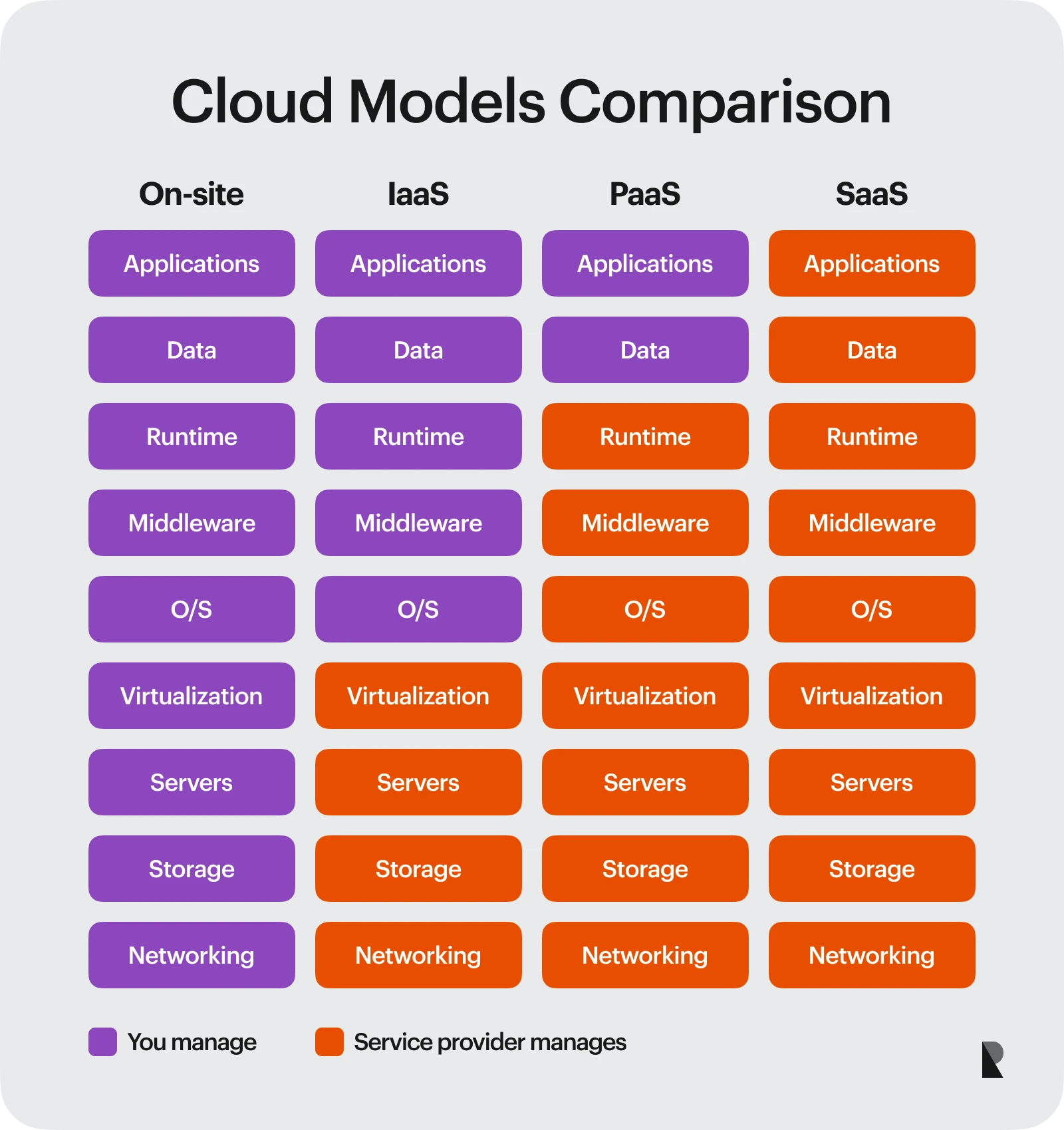
A quick comparison of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS (Leanix)
These factors form the basic ways a SaaS application differentiates from traditional software delivery. Hence, it is a useful model for businesses to manage their software applications online with an underlying infrastructure of a cloud service.
Now that we understand the approaches of a cloud service and SaaS, let’s explore the benefits and examples of each.
Benefits and Examples of SaaS and Cloud Services
SaaS and cloud services are important for businesses to maintain hassle-free online customer access. Let’s dig deeper into the advantages of each and explore some popular examples for better understanding.
Benefits of SaaS
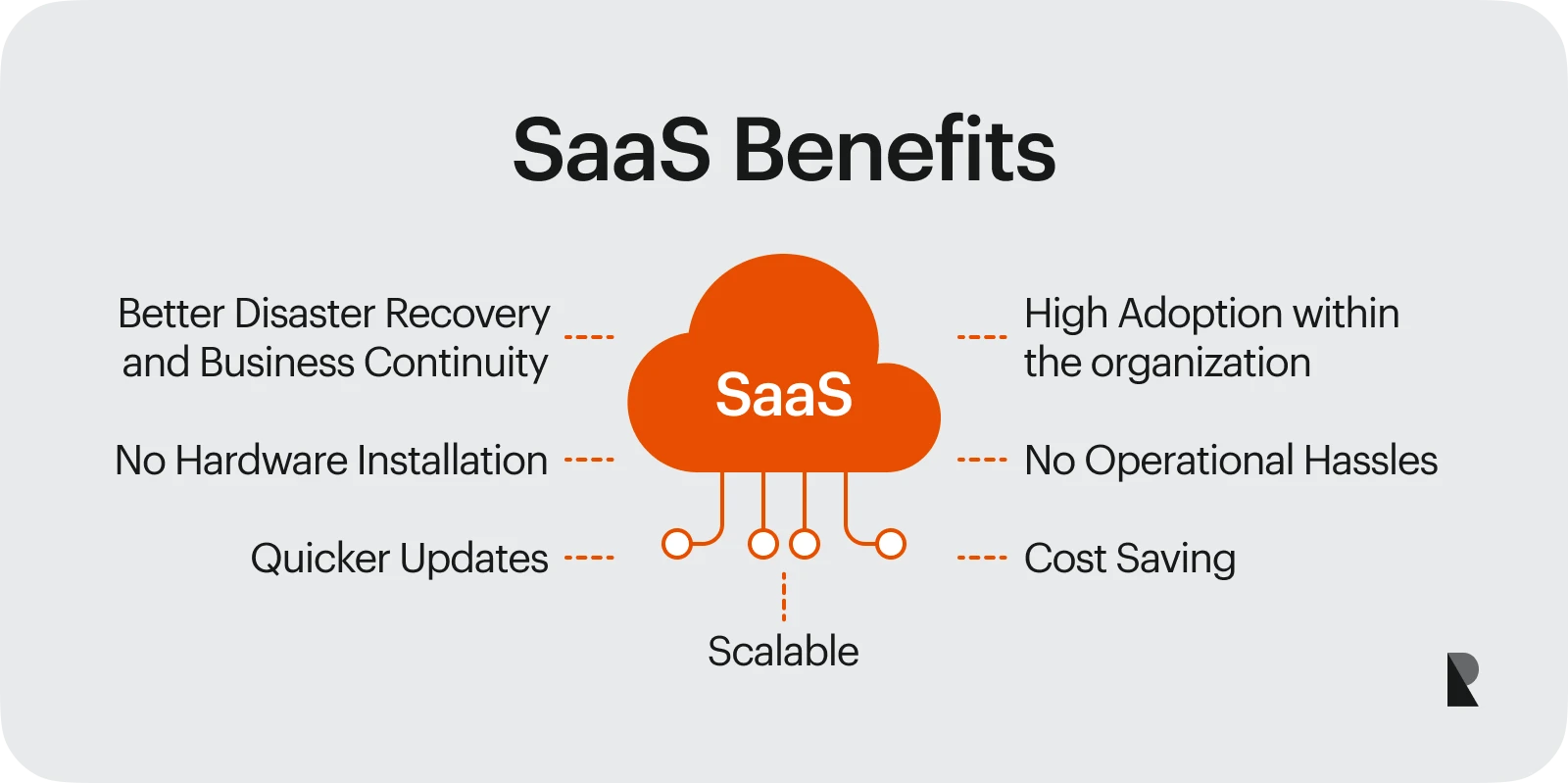
SaaS is a favorable method of software delivery due to its many advantages. Unlike traditional software delivery, SaaS offers cost effectiveness with its subscription plans based on your business usage and eliminating the otherwise huge upfront costs.
It also offers scalability to promote ease in business growth. You simply adjust your SaaS plan to add users or features as required. Plus, it ensures that all updates and security patches are handled by a SaaS provider, ensuring your software is always updated with the latest features and data security.
Most importantly, it offers enhanced accessibility since your SaaS application can be accessed anywhere with an internet connection. In the modern-day, it fosters remote work and easy collaboration, which is why partnering with a web application development company is often a practical step for refining SaaS workflows.
So, if you are a business looking to hire a web app development firm and want to cut costs, SaaS applications can promote a remote work environment. While easy to collaborate and manage, they will also reduce your business's operational costs.
Some common examples of SaaS applications include productivity tools like Gmail and Zoom and CRM software like Salesforce and Hubspot. Plus, there are applications like Shopify for E-commerce and QuickBooks Online for accounting and finance.
The combined package of improved affordability and scalability makes SaaS applications a dominant force in the software industry. It provides a way to empower businesses of all sizes.
Benefits of Cloud Services
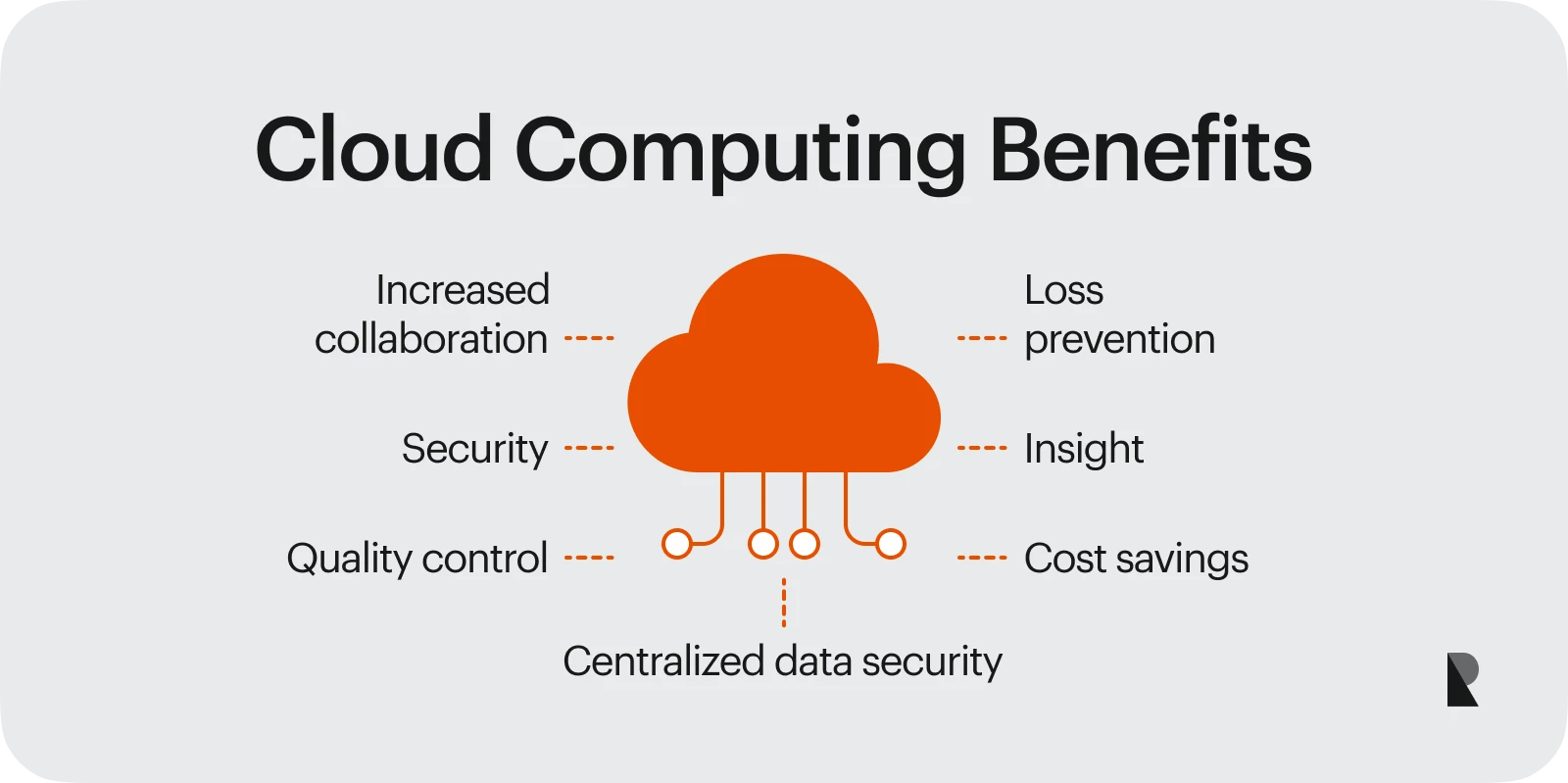
Since SaaS is an extension of cloud-based services, many of the benefits of the two approaches overlap. Cloud service is also a cost-effective approach to handling software applications, as businesses do not require large computing resources to run their apps.
A cloud provider also allows businesses to adjust their plans and computing services according to their requirements, adjusting their payments accordingly. This offers better financial management of business cash flows and improved scalability for expansion.
The ease of execution has even led to the development of cloud-native applications, which are developed and designed to run specifically on a cloud environment. A cloud-native application allows the building of modular microservices that can be run independently and combined as needed.
It promotes flexibility and easier maintenance within a cloud infrastructure, ensuring optimized use of computing resources and other cloud services. It also offers automation of tasks like software application deployment, testing, scaling, and testing.
Some common use cases of cloud services include:
- E-commerce: Businesses can use cloud storage for product images and customer data and cloud-based e-commerce platforms like Shopify to manage their online stores.
- Marketing and Sales: Cloud-based CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software like Salesforce helps businesses manage customer interactions, track leads, and automate marketing campaigns.
- Data Analytics: Cloud platforms provide businesses with powerful data storage and processing capabilities to analyze customer behavior and market trends, and optimize operations.
- Financial Management: Cloud-based accounting software simplifies financial record-keeping, automates tasks, and allows real-time financial data access.
Hence, SaaS applications, cloud-based applications, and cloud-native applications are some infrastructures that allow businesses to improve cost management with their monthly fee-based models.
Plus, these models are run by software vendors, freeing up businesses from the complexity of updating their applications and security measures.
Comparing SaaS and Cloud: Differences and Business Implications
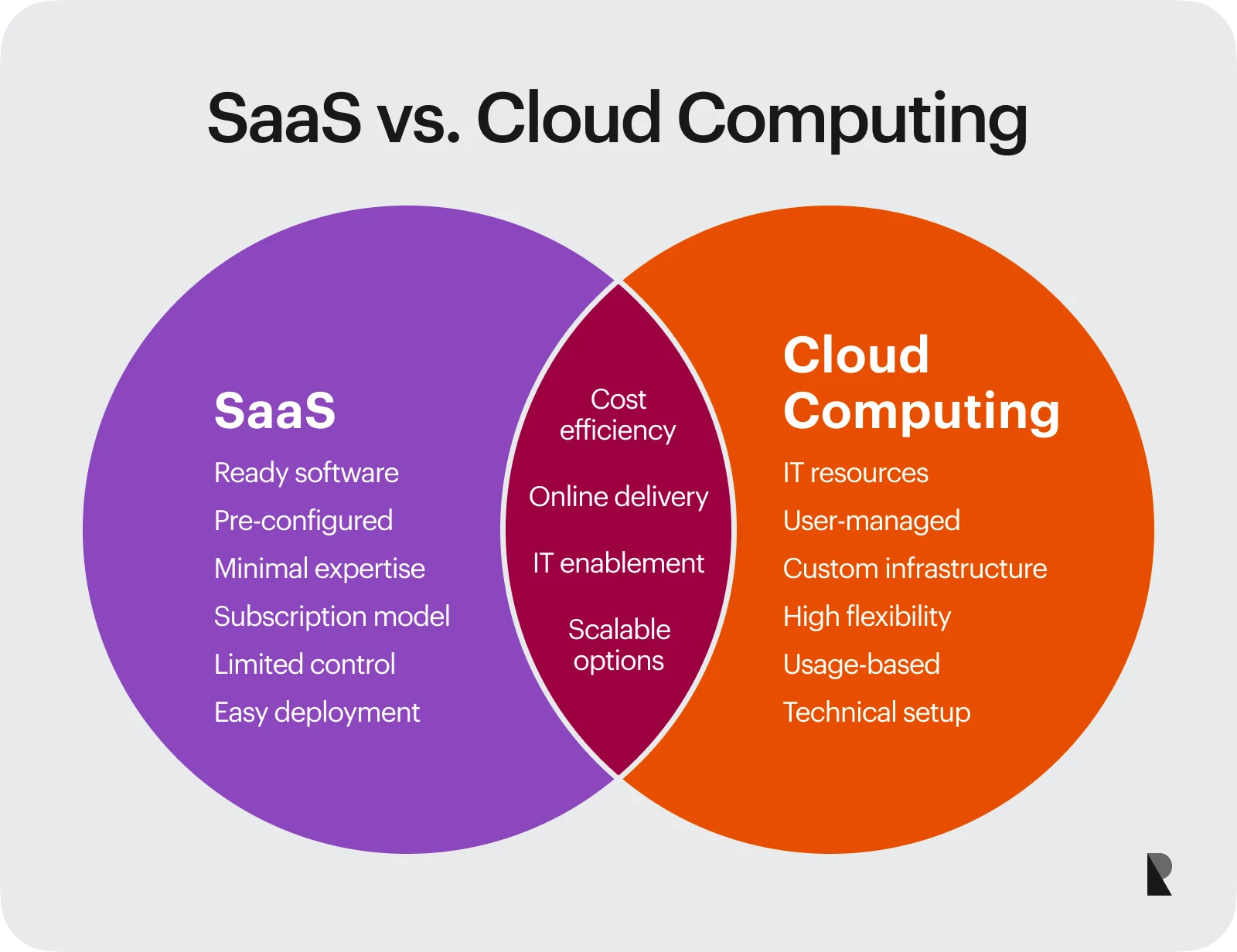
We have elaborately explored the SaaS benefits and advantages of cloud services. While the examples of each highlight the differences in their usage, it is important to better understand the key aspects that make one infrastructure different from the other.
Below is a table comparing SaaS infrastructure with that of a cloud service.
SaaS vs. Cloud Computing Comparison
| Feature | SaaS (Software as a Service) | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Delivers software applications | Offers a wide range of IT resources |
| Examples | Gmail, Salesforce, Dropbox | Virtual Machines, Cloud Storage, Databases |
| Deployment & Control | Pre-configured, limited customization, SaaS provider manages infrastructure | A user configures and manages resources |
| Technical Expertise | Minimal needed | More technical knowledge required |
| Use Case | Ready-to-use software solutions | Diverse IT needs (backups, custom applications) |
| Cost & Management | Predictable subscription fees Less IT management | Variable costs based on usage. Requires a dedicated IT staff |
| Scalability | Scale by choosing different subscription tiers | Scale resources (storage, VMs) up or down |
| Analogy | Pre-built shed (easy to use) | Hardware store with tools and materials (more complex) |
While we understand the differences, there remains a question of choosing the most appropriate approach for your business.
Which Solution is Right for Your Business?
Below are criteria to help you decide between cloud services and SaaS solutions.
Reasons to Choose SaaS Applications
If your business requires a readily available software solution, SaaS applications are a perfect choice as they require minimal setup and are easy to use. Hence, SaaS typically is an ideal choice for applications like CRM and project management.
It also eliminates the need for dedicated in-hours IT staff, so you can operate your SaaS application with limited IT resources. Since your SaaS provider manages all updates and maintenance, the choice becomes more favorable.
It makes SaaS applications easy to use and scale. Plus, the subscription model offers a predictable cost plan, giving you the freedom to proactively manage and grow your business needs.
Reasons to Choose Cloud Computing
While SaaS applications are suitable for a ready-made solution, you must opt for cloud computing for a more customized software solution. Configuring and managing resources to meet your unique requirements offers greater flexibility.
Thus, resulting in greater control over your IT and computing resources. You can configure VMs, manage databases, and choose the software you want to run, making it ideal for businesses with specialized needs.
You can also rely on cloud computing to cater to your fluctuating storage and computing needs. Since cloud providers allow you more freedom to scale your computing resources, it can align well with your frequently changing needs.
Additional Considerations
While the above reasons are specific to each approach of deploying and accessing software applications, there are some general factors to consider when choosing.
- Security - evaluate the specific security measures offered by each solution and ensure they meet your business’s compliance requirements.
- Integration needs - consider how easily the solution can be integrated into your existing IT infrastructure.
- Vendor support - evaluate the level of support offered before making a decision.
Thus, you must evaluate your business needs and software requirements before making the final choice. Both SaaS applications and cloud services have their strengths, you must consider the benefits of each and other additional factors to make an informed decision that best supports your company's growth and success.
Future Trends, Key Takeaways, and Final Thoughts
Modern-day organizations are reliant on information to perform well in the market. Hence, they must collect and maintain large amounts of sensitive data to ensure their competitive advantage. Since cloud providers and SaaS cloud offers solutions for efficient data handling, they will remain relevant solutions in the market.
The future will only bring more innovation in their handling of data and computing resources. With the advent of artificial intelligence (AI), features like data analysis, chatbots, and personalized recommendations have transformed the arena of SaaS and cloud native applications.
Meanwhile, security remains a top priority, with providers enhancing encryption and focusing on compliance. We will also see a rise of sepcialized SaaS catering to specific industries, along with low-code/no-code platforms empowering businesses to build custom applications.
These technological advancements will also result in super apps that offer a range of functionalities for businesses to incorporate in one place. By embracing these trends, businesses can unlock a world of possibilities.
It all starts with making the right choice. While SaaS is your friend for a pre-built software with easy management, cloud is the best choice for high customization with a dedicated IT team. Thus, businesses must choose wisely in this changing landscape where hybrid approaches are becoming increasingly popular.
Jul 4, 2024
